Treatment Overview
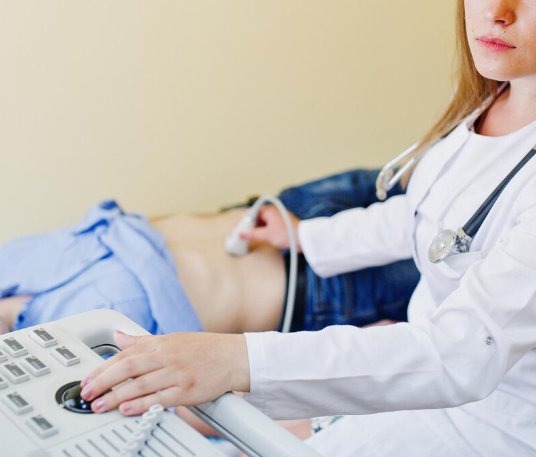
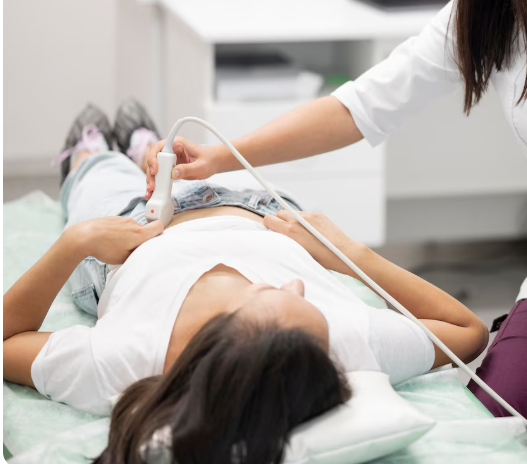
Gynecologic ultrasound for pelvic pain is a non-invasive diagnostic procedure that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce detailed images of the female pelvic organs, including the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and surrounding structures. It is an essential tool in evaluating the causes of pelvic pain, which can range from benign conditions such as ovarian cysts to complex disorders like endometriosis or pelvic inflammatory disease.
In Korea, gynecologic ultrasound has evolved into a precise and patient-friendly diagnostic method, utilizing the latest imaging technology, such as three-dimensional (3D) and high-resolution transvaginal ultrasound. This enables gynecologists to detect abnormalities earlier and more accurately. Korea’s integration of advanced ultrasound techniques with specialized women’s healthcare has positioned the country as a leading destination for pelvic pain evaluation.
Purpose & Benefits
The purpose of gynecologic ultrasound in pelvic pain evaluation is to provide a clear, accurate, and real-time view of the pelvic anatomy to identify structural or pathological causes of pain. Benefits of undergoing this evaluation in Korea include:
- Accurate diagnosis: Advanced ultrasound machines and expert interpretation allow for precise detection of cysts, fibroids, endometriotic lesions, or pelvic adhesions.
- Non-invasive and painless: Ultrasound does not require incisions or radiation, ensuring patient comfort and safety.
- Immediate results: Many Korean clinics provide same-day results and consultations.
- Cost-effectiveness: Ultrasound is relatively affordable compared to other imaging techniques like MRI or CT scans.
For patients in Korea, this procedure is often the first step in a broader pelvic pain assessment strategy, offering both clarity and efficiency.
Ideal Candidates
Gynecologic ultrasound is suitable for women experiencing:
- Chronic or acute pelvic pain.
- Unexplained menstrual irregularities.
- Pain during intercourse.
- Infertility concerns.
- History of ovarian cysts or fibroids.
In Korea, this service is available to both residents and international patients, with many clinics offering English-speaking specialists and personalized care plans tailored to patient needs.
Possible Risks & Complications
Gynecologic ultrasound is considered safe, but minor discomfort may occur, especially during transvaginal ultrasound where a probe is inserted into the vagina. Other considerations include:
- Mild cramping during the procedure.
- Slight discomfort from pressure applied by the transducer.
- Rarely, temporary spotting.
Korean medical facilities minimize any risks through professional technique, advanced probe design, and patient-centered care.
Techniques Used
Korean clinics use various ultrasound techniques to evaluate pelvic pain, including:
- Transabdominal ultrasound: Ideal for a general pelvic overview, using the probe over the lower abdomen.
- Transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS): Provides higher resolution imaging of the uterus, ovaries, and endometrium.
- 3D ultrasound: Offers detailed multiplanar views for better evaluation of complex pelvic structures.
- Doppler ultrasound: Measures blood flow to detect vascular changes or inflammation.
These advanced methods allow Korean gynecologists to detect even subtle abnormalities, enhancing diagnostic precision.
Recovery & Aftercare
Gynecologic ultrasound is non-invasive, requiring no recovery period. Patients can resume daily activities immediately after the procedure. Aftercare may include:
- Reviewing results with the gynecologist.
- Planning further diagnostic tests or treatment if necessary.
- Lifestyle or dietary recommendations to support pelvic health.
Korean clinics ensure that patients receive clear explanations of their ultrasound findings and detailed guidance for next steps.
Results & Longevity
Ultrasound provides real-time imaging results that can be discussed immediately during the consultation. For ongoing pelvic pain, results may lead to additional diagnostic procedures such as MRI, hysteroscopy, or laparoscopy for definitive diagnosis.
Gynecologic ultrasound results are reliable for immediate diagnosis, but follow-up evaluations may be necessary for chronic conditions, ensuring long-term monitoring and effective pain management.
Treatment Process in Korea
In Korea, the process for gynecologic ultrasound begins with a detailed consultation and medical history review. The ultrasound may be performed transabdominally, transvaginally, or using a combination, depending on the patient’s symptoms and history.
Korean medical facilities stand out for their use of the latest ultrasound technologies, including high-resolution 3D imaging and Doppler analysis, offering unparalleled diagnostic accuracy. Patient comfort is prioritized, with multilingual support, private examination rooms, and efficient scheduling.
Korea’s healthcare excellence in women’s health, combined with the latest imaging innovations, has made the country a global leader in gynecologic ultrasound and pelvic pain evaluation.
Cost Range
The cost of gynecologic ultrasound in Korea depends on the type and complexity of the procedure:
- Basic transabdominal ultrasound: ₩100,000–₩200,000 KRW ($80–$160 USD).
- Transvaginal ultrasound: ₩150,000–₩300,000 KRW ($120–$240 USD).
- 3D ultrasound with Doppler: ₩250,000–₩500,000 KRW ($200–$400 USD).
Many clinics also offer packages combining ultrasound with consultation and additional tests, ranging from ₩400,000–₩900,000 KRW ($320–$720 USD).
Popular Clinics in Korea
- Samsung Medical Center — Leading in advanced 3D pelvic ultrasound diagnostics.
- Asan Medical Center — Comprehensive pelvic pain evaluation with multidisciplinary care.
- CHA Bundang Women’s Hospital — Specializes in gynecologic imaging and minimally invasive diagnosis.
- Severance Hospital, Yonsei University — Utilizes high-definition transvaginal and Doppler ultrasound.
- Kyung Hee University Medical Center — Expert pelvic pain diagnostics with innovative imaging technology.