Treatment Overview
Overactive bladder (OAB) is a condition marked by a sudden, uncontrollable urge to urinate, often accompanied by frequent urination and sometimes urinary incontinence. In Korea, OAB treatment combines advanced medical technology with patient-centered care to provide effective symptom relief and improve quality of life. Korean clinics use a holistic approach that includes medical therapy, behavioral interventions, and minimally invasive procedures tailored to individual patient needs.
Purpose & Benefits
The main purpose of OAB treatment is to reduce urinary urgency, frequency, and incontinence, thereby improving daily comfort and overall quality of life.
Benefits of treatment in Korea include:
- Relief from bothersome urinary symptoms, enabling normal daily activities.
- Prevention of complications such as urinary tract infections and kidney damage.
- Personalized treatment plans using the latest medications, therapies, and minimally invasive techniques.
- Access to internationally accredited hospitals with experienced urologists.
By receiving treatment in Korea, patients can experience rapid improvement in symptoms while benefiting from advanced diagnostic and therapeutic technology.
Ideal Candidates
OAB treatment in Korea is recommended for individuals who:
- Experience frequent urination (more than eight times per day).
- Have strong, sudden urges to urinate, often leading to incontinence.
- Wake frequently at night to urinate (nocturia).
- Have symptoms that interfere with work, social life, or sleep quality.
Men and women of all ages can seek treatment, especially those over 40, or those with underlying conditions such as diabetes, neurological disorders, or prior pelvic surgery.
Possible Risks & Complications
OAB treatments in Korea are generally safe, but potential risks include:
- Mild side effects from medications, such as dry mouth, constipation, or dizziness.
- Temporary urinary retention following bladder injections or minimally invasive procedures.
- Rare complications such as infection or bleeding from catheter-based interventions.
Korean hospitals minimize risks through careful patient evaluation, sterile techniques, and thorough follow-up care.
Techniques & Technology Used
Korea uses a wide range of modern techniques to treat OAB effectively:
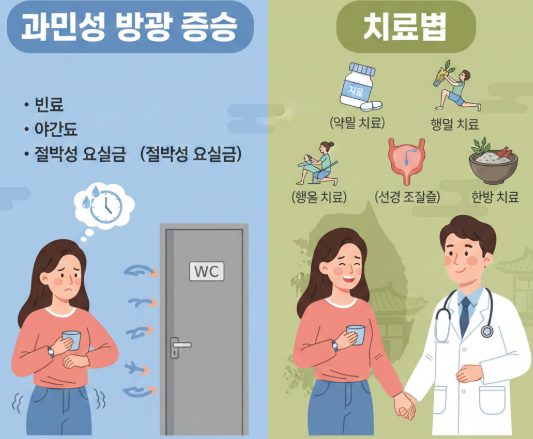
- Medication Therapy: Antimuscarinics and beta-3 agonists reduce bladder overactivity.
- Behavioral Therapy: Bladder training, pelvic floor exercises, and fluid management strategies.
- Neuromodulation Therapy: Electrical stimulation of nerves controlling the bladder to reduce urgency.
- Botulinum Toxin (Botox) Injections: Minimally invasive procedure to relax overactive bladder muscles.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery: For severe cases, including bladder augmentation or sling procedures.
- Advanced Monitoring: Urodynamic tests and bladder scans to guide treatment decisions.
Korean clinics integrate technology with expert care to maximize treatment efficacy and minimize discomfort.
Treatment Process in Korea
The OAB treatment process in Korea is structured to ensure optimal results:
- Initial Consultation: A urologist evaluates symptoms, medical history, and lifestyle factors.
- Diagnostic Testing: Urinalysis, blood tests, bladder diaries, urodynamic studies, and imaging tests are performed as needed.
- Treatment Planning: Doctors create a personalized plan, selecting medication, behavioral therapy, or procedural interventions based on severity.
- Therapy Implementation: Patients begin their prescribed treatment, whether medication, exercises, or minimally invasive procedures.
- Follow-Up Care: Continuous monitoring and adjustments ensure optimal outcomes and long-term symptom control.
International patients benefit from English-speaking coordinators, online consultation options, and streamlined hospital services for smooth treatment experiences.
Recovery & After-Care
Recovery from OAB treatment in Korea depends on the type and severity of intervention:
- Medication Therapy: Most patients notice improvement within weeks, with minimal recovery requirements.
- Behavioral Therapy: Ongoing practice of bladder training and pelvic floor exercises improves bladder control over time.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Patients may experience mild discomfort for a few days but can usually resume normal activities quickly.
After-care includes lifestyle adjustments such as fluid management, diet changes, and pelvic exercises. Korean hospitals provide regular follow-up and guidance to ensure long-lasting results.
Results & Longevity
Patients who undergo OAB treatment in Korea can expect:
- Significant reduction in urinary urgency and frequency.
- Improved sleep and reduced nocturia.
- Enhanced confidence and quality of life.
- Long-term management plans that prevent recurrence and maintain bladder health.
With adherence to therapy and lifestyle recommendations, the benefits of treatment can last for years, and ongoing check-ups help sustain results.
Why Korea Is a Top Destination
Korea has become a preferred destination for OAB treatment due to:
- Advanced Medical Facilities: Cutting-edge technology for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
- Expert Specialists: Highly skilled urologists trained in international techniques.
- Patient-Centered Care: Integrated services including diagnostics, therapy, and follow-up care.
- Affordability: Competitive treatment costs compared to Western countries.
- Medical Tourism Support: English-speaking coordinators, travel assistance, and comfortable hospital stays.
Patients can combine top-quality healthcare with cultural experiences, making Korea an attractive choice for international medical travelers.
Cost Range
The cost of OAB treatment in Korea varies depending on treatment type:
- Medication therapy: $100 – $300 per month
- Behavioral therapy: $50 – $150 per session
- Botox injections: $600 – $1,000 per treatment
- Minimally invasive procedures: $1,000 – $3,000
Many hospitals offer packages for international patients, covering consultation, diagnostics, treatment, and aftercare for transparency and convenience.
Popular Clinics in Korea
Leading hospitals and clinics for OAB treatment in Korea include:
- Samsung Medical Center, Seoul
- Asan Medical Center, Seoul
- Severance Hospital (Yonsei University), Seoul
- Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul
- CHA Bundang Medical Center, Seongnam
These institutions are internationally accredited, provide English-speaking support, and have specialized urology departments experienced in managing OAB for both local and international patients.