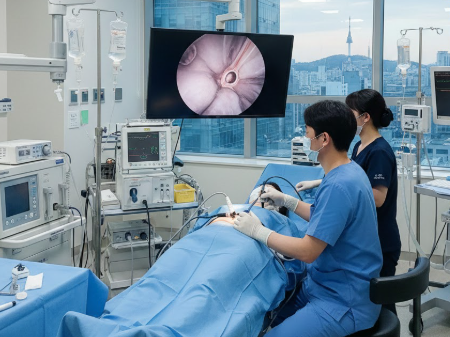
Treatment Overview
Cystoscopy, commonly known as bladder endoscopy, is a minimally invasive diagnostic and treatment procedure used to examine the interior of the bladder and urethra. It allows urologists to detect abnormalities such as bladder stones, tumors, inflammation, or structural issues. In Korea, cystoscopy is performed using advanced flexible or rigid endoscopes, offering high-definition imaging for precise diagnosis. This procedure can be both diagnostic and therapeutic, depending on patient needs.
Purpose & Benefits
The main purpose of cystoscopy is to identify and address urinary tract issues early, ensuring proper management of bladder and urethral conditions. Key benefits include:
- Early detection of bladder cancer, stones, and infections.
- Minimally invasive procedure with reduced discomfort compared to surgical exploration.
- Ability to perform minor interventions like stone removal or tissue biopsy during the procedure.
- Quick recovery and minimal downtime, making it suitable for international patients.
- Enhanced accuracy with modern imaging technologies used in Korea.
Ideal Candidates
Cystoscopy is recommended for individuals experiencing:
- Blood in urine (hematuria) without an apparent cause.
- Recurrent urinary tract infections or persistent bladder symptoms.
- Chronic pelvic pain or unexplained lower urinary tract symptoms.
- Suspected bladder tumors or abnormal imaging results.
- Need for bladder stone evaluation or removal.
Patients should undergo a thorough consultation with a Korean urologist to confirm suitability for the procedure.
Possible Risks & Complications
Cystoscopy is generally safe, but like all medical procedures, it carries potential risks, including:
- Mild discomfort or burning sensation during urination post-procedure.
- Temporary blood in urine or minor bleeding from biopsy sites.
- Urinary tract infection, which is rare but treatable with antibiotics.
- Rarely, bladder perforation may occur, requiring additional care.
Korean hospitals follow strict safety protocols to minimize risks and ensure patient safety, making cystoscopy a reliable option.
Techniques & Technology Used
Korea is renowned for using state-of-the-art medical equipment in cystoscopy:
- Flexible Cystoscopy: Thin, bendable scopes for less discomfort and outpatient procedures.
- Rigid Cystoscopy: Provides high-definition imaging for precise diagnosis and minor interventions.
- High-Definition Camera Systems: Allow real-time visualization of bladder walls and urethra.
- Laser Technology: Used for stone removal or minor lesion ablation during cystoscopy.
These advanced techniques ensure accurate diagnosis, minimal invasiveness, and better patient outcomes.
Treatment Process in Korea
The cystoscopy procedure in Korea typically involves:
- Pre-procedure Evaluation: Blood tests, urine analysis, and imaging to assess patient condition.
- Preparation: Local or general anesthesia depending on the case and patient comfort.
- Procedure: Insertion of the cystoscope through the urethra to examine the bladder. Biopsies or minor treatments may be performed simultaneously.
- Post-procedure Monitoring: Short observation period to check for complications, usually allowing same-day discharge.
Korean hospitals ensure a comfortable environment for international patients, including translation services and dedicated coordinators.
Recovery & After-Care
Recovery after cystoscopy is generally quick, with most patients resuming normal activities within 24–48 hours. Key after-care instructions include:
- Drinking plenty of water to flush the urinary tract.
- Avoiding strenuous physical activity for a few days.
- Monitoring for symptoms like persistent bleeding, fever, or severe pain.
- Following prescribed medications, including antibiotics if recommended.
Korean medical facilities provide clear after-care guidelines and follow-up consultations to ensure complete recovery.
Results & Longevity
Cystoscopy offers immediate and reliable results, enabling urologists to diagnose bladder conditions accurately. When therapeutic interventions are performed, such as stone removal or lesion ablation, results are long-lasting with minimal recurrence if proper follow-up care is maintained. Regular cystoscopy may be recommended for patients at high risk of bladder cancer or recurrent stones.
Why Korea Is a Top Destination
Korea has become a global hub for urology care due to:
- Advanced Technology: High-definition cystoscopes and laser treatments.
- Experienced Specialists: Board-certified urologists with international experience.
- Efficient Healthcare System: Short waiting times and streamlined procedures.
- Medical Tourism Services: Comprehensive packages including hospital transfers, translation, and accommodation.
- Affordable Costs: Competitive pricing compared to Western countries without compromising quality.
These factors make Korea an ideal choice for international patients seeking safe, effective, and comfortable cystoscopy procedures.
Cost Range
The cost of cystoscopy in Korea varies depending on the type (diagnostic or therapeutic) and hospital:
- Diagnostic Cystoscopy: $400 – $800 USD
- Therapeutic Cystoscopy (stone removal or biopsy): $800 – $1,500 USD
Packages for international patients often include hospital fees, accommodation, and interpreter services.
Popular Clinics in Korea
Some of the most reputable hospitals and clinics for cystoscopy in Korea include:
- Severance Hospital, Seoul – Advanced urology department with international patient services.
- Asan Medical Center, Seoul – Offers cutting-edge diagnostic and therapeutic cystoscopy.
- Samsung Medical Center, Seoul – Renowned for minimally invasive bladder procedures.
- Bundang CHA Hospital, Seongnam – Specializes in outpatient cystoscopy with patient-focused care.
- Hanyang University Hospital, Seoul – Comprehensive urology treatments for domestic and international patients.
These clinics combine high medical standards with personalized care for medical tourists.