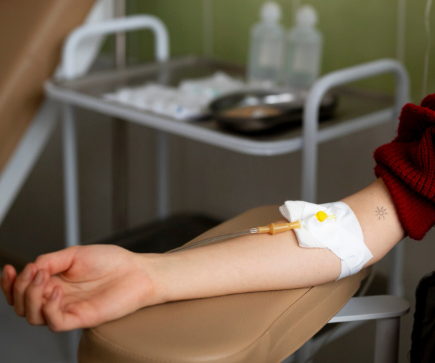
Stem cell therapy is one of the most promising medical breakthroughs in regenerative medicine, offering potential healing for injuries, age-related degeneration, and chronic conditions. But how does it actually work?
Whether you’re exploring this treatment for cosmetic, orthopedic, or wellness purposes—especially in cutting-edge destinations like South Korea—this guide will help you understand the science behind regeneration and what makes stem cell therapy so revolutionary.
🌱 What Are Stem Cells, Exactly?
Stem cells are undifferentiated, “blank slate” cells that have two key properties:
- Self-Renewal
They can divide and produce identical copies of themselves indefinitely. - Differentiation
They can transform into specialized cells—like muscle, nerve, cartilage, or skin cells—depending on the body’s needs.
These unique characteristics make stem cells vital for repairing and regenerating damaged tissues.
🔄 The Body’s Natural Healing System
When your body is injured or aging, it naturally sends repair signals to stimulate healing. However, with age or chronic disease, the body’s ability to regenerate slows down.
This is where stem cell therapy comes in—it acts as a bio-boost to enhance your body’s ability to heal and regenerate by delivering fresh, potent stem cells directly to the area in need.
⚙️ How Stem Cell Therapy Works – Step-by-Step
1. Harvesting the Stem Cells
Stem cells are collected from one of the following sources:
- Autologous (Your own body):
- Adipose tissue (fat) – common and rich in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)
- Bone marrow – less commonly used but valuable in orthopedic treatments
- Allogeneic (Donor source):
- Umbilical cord blood – ethically donated and processed
- Placenta or amniotic fluid – rich in growth factors and stem cells
In Korea, clinics use highly regulated lab environments to isolate, purify, and sometimes culture these cells for higher concentrations.
2. Processing and Activation
After harvesting, stem cells undergo:
- Centrifugation or enzymatic processing to extract pure stem cells
- Activation using growth factors, sometimes combined with PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) or exosomes to enhance their healing effects
The result is a potent, injectable cell suspension ready for targeted therapy.
3. Delivery to Targeted Area
The stem cell solution is carefully injected into the affected area, such as:
- Knee or joint for arthritis
- Face or scalp for skin rejuvenation or hair regrowth
- IV infusion for systemic anti-aging or immune support
Doctors use ultrasound or imaging to guide placement and ensure precision.
4. Regeneration and Healing
Once introduced, stem cells:
- Reduce inflammation by modulating the immune response
- Stimulate collagen and elastin production (in aesthetic treatments)
- Promote angiogenesis – the formation of new blood vessels
- Replace damaged or dying cells with new, functional tissue
Over the following weeks and months, patients typically see gradual, natural-looking improvements in function, appearance, and comfort.
🧬 Types of Stem Cells Used in Therapy
| Type | Description | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) | Found in fat, bone marrow, umbilical cord; known for anti-inflammatory & tissue-repair abilities | Joints, skin, hair, autoimmune |
| Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs) | Found in bone marrow and cord blood; primarily generate blood cells | Blood disorders, research use |
| Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs) | Lab-engineered from adult cells to act like embryonic stem cells | Experimental; not widely used clinically |
| Embryonic Stem Cells (ESCs) | Derived from embryos; highly versatile but ethically sensitive | Research stage only (not used in Korea clinically) |
Most treatments are done in a single session but may require a series of 2–4 sessions for optimal and lasting results.
🧪 What Enhances Stem Cell Therapy?
Stem cell therapy in Korea is often paired with:
| Combination | Benefit |
|---|---|
| PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) | Adds growth factors to speed up healing |
| Exosomes | Boosts cell communication and regeneration |
| Laser or RF Microneedling | Opens channels for stem cell absorption |
| NAD+ IV Drips | Enhances cellular energy and longevity |
| Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy | Increases oxygen delivery to healing tissues |
🧷 Is It Safe?
When performed by qualified professionals in licensed facilities, stem cell therapy is considered safe. Minimal side effects include:
- Mild swelling or redness at injection site
- Temporary fatigue (after IV therapy)
- Rare allergic reaction (more likely in donor cells)
Korean clinics are highly regulated and follow rigorous standards for cell safety, purity, and traceability.
🌏 Why Korea Excels in Stem Cell Science
South Korea is a global hub for regenerative medicine, known for:
- Advanced stem cell labs and biotech innovations
- Fast regulatory approval for proven therapies
- Seamless integration of medical tourism services
- Clinics that offer custom protocols tailored to international patients
🧭 Summary: The Science of Healing, Reimagined
Stem cell therapy works by harnessing your body’s own healing intelligence, boosting it with concentrated regenerative power. Whether you’re treating aging skin, painful joints, or chronic conditions, this therapy provides a non-surgical, scientifically backed path to renewal.