Treatment Overview
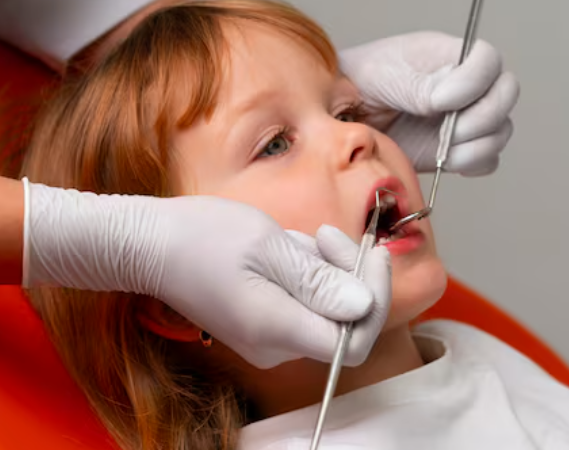
Anterior Tooth Restoration in Korea focuses on restoring the front (anterior) teeth of children with advanced precision, aesthetic detail, and comfort. These treatments address issues such as fractures, decay, discoloration, and enamel defects using modern materials and minimally invasive techniques tailored to pediatric needs.
Korean pediatric dental clinics emphasize preserving natural tooth structure and promoting long-term oral health, employing advanced resin composites, glass ionomers, and digital bonding technologies. The approach balances function, appearance, and child comfort—ensuring a natural smile that supports speech, chewing, and confidence during growth.
With Korea’s renowned digital dentistry, pain management systems, and child-focused care, anterior tooth restoration becomes a smooth, anxiety-free experience for young patients and parents alike.
Purpose & Benefits
The primary goal of anterior tooth restoration is to restore function and beauty to damaged or decayed front teeth while maintaining child comfort and tooth integrity.
Purpose:
- To repair chipped, fractured, or decayed anterior (front) teeth.
- To enhance the smile’s appearance and symmetry.
- To maintain proper speech development and chewing efficiency.
- To protect developing permanent teeth and support jaw growth.
- To prevent further enamel or dentin damage.
Benefits:
- Natural Aesthetics: Tooth-colored materials blend seamlessly with surrounding teeth.
- Pain-Free Treatment: Korean pediatric dentists use advanced anesthesia and laser-assisted care for minimal discomfort.
- Minimally Invasive: Conserves maximum healthy tooth structure.
- Durable & Safe Materials: Biocompatible composites and glass ionomers suitable for children.
- Confidence Restoration: Improves smile and social confidence during early development.
- Preventive Advantage: Protects remaining tooth structure and supports long-term dental health.
These benefits make anterior tooth restoration an essential part of pediatric aesthetic dentistry in Korea.
Ideal Candidates
Anterior tooth restoration is suitable for children requiring aesthetic and functional repair of their front teeth due to decay, trauma, or developmental defects.
Ideal Candidates Include:
- Children with fractured or chipped front teeth.
- Those with early childhood caries or discoloration.
- Kids with enamel hypoplasia or mild malformation.
- Patients with accidental dental injuries (e.g., sports trauma).
- Children requiring cosmetic correction for confidence or speech clarity.
Korean pediatric dentists ensure that each case is evaluated individually for safety, comfort, and long-term oral harmony.
Possible Risks & Complications
Anterior restorations are safe and highly successful in children, though minor concerns can occasionally occur:
- Tooth Sensitivity: Temporary after bonding or preparation.
- Restoration Wear or Discoloration: Possible over time, especially with staining foods.
- Bond Failure: Rare, but may occur with poor oral hygiene or trauma.
- Gum Irritation: Mild and temporary if plaque accumulates near restorations.
Korean dental professionals use child-safe materials, laser curing, and precision bonding to minimize these risks, ensuring strong and lasting restorations.
Techniques Used
Korean pediatric dentists combine artistry and advanced dental technology for durable, aesthetic anterior restorations.
Common Techniques Include:
- Digital 3D Scanning (CAD/CAM): For accurate tooth shape and alignment analysis.
- Composite Resin Bonding: Uses nano-hybrid or flowable composites for natural aesthetics.
- Strip Crowns (for Children): Transparent molds filled with composite resin for uniform tooth shape.
- Glass Ionomer Restorations: For fluoride release and decay prevention.
- Laser-Assisted Cavity Preparation: Minimizes pain, noise, and anxiety for young patients.
- Polishing & Finishing: Achieves a smooth, glossy surface mimicking natural enamel.
These modern techniques ensure that Korean pediatric restorations are precise, long-lasting, and child-friendly.
Recovery & Aftercare
Recovery from anterior tooth restoration is typically immediate and painless.
Aftercare Guidelines:
- Avoid biting hard foods (like ice or candy) for 24–48 hours.
- Maintain daily brushing with fluoride toothpaste.
- Schedule checkups every 6 months for evaluation and polishing.
- Use mouthguards during sports to protect restored teeth.
- Encourage good oral habits to prevent secondary decay.
Following these steps ensures the restoration maintains its strength, color, and comfort for years.
Results & Longevity
Korean anterior restorations provide both instant aesthetic enhancement and functional durability.
Expected Results:
- Natural color match with adjacent teeth.
- Restored confidence in speech and smiling.
- Smooth enamel-like finish resistant to wear.
- Reinforced tooth structure with protective bonding.
- Lifespan: 3–10 years, depending on material and care.
With Korean expertise and material innovation, pediatric restorations remain beautiful and strong throughout growth stages.
Treatment Process in Korea
Korean dental clinics follow a systematic, child-focused approach to ensure comfort, precision, and safety.
Step-by-Step Process:
- Consultation & Diagnosis: Pediatric dentist assesses the affected tooth with X-rays and intraoral scans.
- Treatment Planning: Selection of material (composite, glass ionomer, or strip crown).
- Tooth Preparation: Minimal cleaning and shaping using laser or micro burs.
- Shade Matching: Ensures color harmony with natural teeth.
- Material Application: Layered resin or crown placement for optimal shape and function.
- Curing & Polishing: Light-cured and polished for natural gloss.
- Final Evaluation: Dentist checks bite, comfort, and child’s satisfaction.
This process is efficient, pain-free, and designed to keep children calm and cooperative throughout.
Why Korea Is a Top Destination
Korea stands out in pediatric anterior restoration for its innovation, gentle approach, and world-class materials.
- Certified Pediatric Specialists: Experts trained in child psychology and behavior management.
- Advanced Digital Systems: 3D scanning, CAD/CAM fabrication, and laser tools.
- Minimally Invasive Philosophy: Focus on tooth preservation and child comfort.
- Affordable Excellence: Global-quality care at competitive pricing.
- Comprehensive Aftercare: Regular checkups, fluoride applications, and oral health education.
Korean pediatric dentistry combines clinical precision with compassionate care, making it a preferred choice worldwide.
Unique Korean Methods & Technology
- AI-Enhanced Smile Design: Predicts restoration outcomes for natural harmony.
- Laser-Assisted Bonding: Reduces discomfort and increases adhesion strength.
- Nano-Filled Composite Technology: Enhances color stability and durability.
- Digital Shade Matching Systems: Ensures perfect color blending with natural teeth.
- Sedation & Distraction Dentistry: Child-friendly environments with audiovisual comfort tools.
These innovations define Korea’s global leadership in pediatric aesthetic dentistry.
Cost Range
The cost of Anterior Tooth Restoration in Korea varies based on the type of restoration, materials used, and clinical complexity.
- Composite Restoration (per tooth): ₩80,000 – ₩180,000 (USD $60 – $140)
- Strip Crown Restoration: ₩150,000 – ₩300,000 (USD $110 – $230)
- Glass Ionomer Restoration: ₩100,000 – ₩200,000 (USD $75 – $150)
- Comprehensive Pediatric Aesthetic Package: ₩500,000+ (USD $380+)
Most clinics include consultation, anesthesia, 3D scanning, and polishing in their treatment packages.
Popular Clinics
- Seoul National University Dental Hospital (Pediatric Department): Renowned for aesthetic and preventive pediatric dentistry.
- Yonsei University Severance Dental Hospital: Specializes in digital resin bonding and strip crown systems.
- Asan Medical Center Dental Clinic: Offers laser-assisted, minimally invasive treatments.
- Samsung Medical Dental Center (Children’s Care Unit): Focuses on advanced pain-free restoration methods.
- MizMedi Pediatric Dental Clinic: Expert in cosmetic and trauma-related anterior restorations.