Treatment Overview
Kidney stones are solid deposits of minerals and salts that form in the kidneys, causing flank pain, hematuria, and urinary obstruction. Accurate diagnosis and localization are crucial for effective treatment planning.
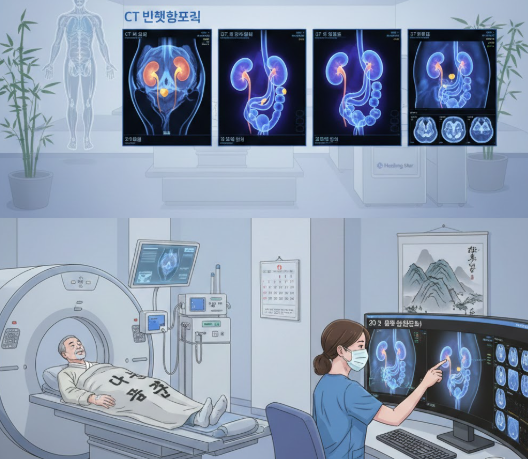
CT urography is an advanced imaging technique that provides detailed 3D images of the kidneys, ureters, and bladder. Korea offers high-quality CT urography services combined with expert urologist evaluation for precise diagnosis and treatment planning, making it ideal for both local and international patients.
Purpose & Benefits
The primary purpose of CT urography is to detect kidney stones, evaluate their size and location, and assess the urinary tract for obstruction or other abnormalities. Key benefits include:
- High-resolution, detailed imaging of kidneys, ureters, and bladder
- Accurate detection of small or complex stones not visible on X-ray or ultrasound
- Assessment of urinary tract obstruction and kidney function
- Quick, non-invasive procedure with immediate results
- Ideal for patients with recurrent or complicated stones
- Comprehensive care for international patients, including English-speaking support
Ideal Candidates
CT urography is suitable for patients who:
- Have severe or recurrent flank pain
- Present with hematuria (blood in urine)
- Have a history of kidney stones that are difficult to detect on ultrasound or X-ray
- Are at high risk of urinary tract obstruction
- Require preoperative planning for minimally invasive stone removal
- International patients seeking accurate and detailed diagnostic imaging
Possible Risks & Complications
CT urography is generally safe, but considerations include:
- Exposure to low-dose ionizing radiation
- Rare allergic reaction to contrast agents (if used)
- Mild discomfort from lying still during the scan
- Caution in patients with kidney impairment when contrast is used
Despite these minor risks, the benefits of detailed imaging and precise treatment planning outweigh the potential drawbacks.
Techniques & Technology Used
Korean hospitals utilize state-of-the-art CT urography technology:
High-Resolution CT Scanner – Captures detailed cross-sectional images of kidneys, ureters, and bladder.
Contrast-Enhanced CT – Enhances visualization of urinary tract structures and stones.
3D Reconstruction Imaging – Provides three-dimensional views for surgical planning.
Low-Dose CT Protocols – Reduces radiation exposure while maintaining image quality.
Integration with Other Diagnostics – Results are combined with urine analysis, blood tests, and ultrasound for a comprehensive evaluation.
Advanced Software – Enables accurate measurement of stone size, density, and location, crucial for treatment decisions.
These technologies ensure precise detection and evaluation of kidney stones.
Treatment Process in Korea
The CT urography process for kidney stones in Korea includes:
- Initial Consultation
Specialists review medical history, symptoms, and previous imaging studies. - Preparation for Scan
Patients may be instructed to fast or hydrate depending on contrast use. - CT Urography Imaging
The patient lies on the scanning table while high-resolution images are captured. The procedure typically takes 15–30 minutes. - Image Analysis
Radiologists and urologists review images to assess stone size, location, density, and any urinary obstruction. - Diagnosis & Treatment Planning
Based on CT findings, physicians may recommend:- Observation for small or asymptomatic stones
- Medication to facilitate stone passage
- Minimally invasive procedures like ureteroscopy, laser lithotripsy, or percutaneous nephrolithotomy
- Preventive strategies for recurrent stone formation
- Follow-Up & Monitoring
CT urography may be repeated in follow-ups to monitor stone resolution or post-treatment outcomes.
Recovery & After-Care
CT urography is non-invasive, and patients can:
- Resume normal activities immediately
- Stay hydrated to support kidney and urinary tract health
- Follow dietary or medication recommendations based on findings
For patients undergoing treatment, recovery varies: - Observation or medication: immediate return to normal activity
- Minimally invasive procedures: 1–3 days
- Surgical interventions: 1–2 weeks
Korean hospitals provide clear post-procedure guidance, particularly for international patients.
Results & Longevity
CT urography provides highly accurate results for kidney stone evaluation:
- Early detection and precise localization of stones
- Detailed assessment of urinary tract obstruction
- Guidance for tailored treatment and preventive strategies
- Long-term monitoring for recurrent stones
Korea’s advanced CT technology and expert urologists ensure reliable diagnosis and long-lasting patient outcomes.
Why Korea Is a Top Destination
Korea is a preferred destination for CT urography and kidney stone evaluation due to:
- High-quality CT scanners with advanced imaging protocols
- Expert radiologists and urologists with extensive experience in stone management
- Rapid, accurate diagnostic results
- Integration with comprehensive treatment planning
- Minimally invasive intervention options for stone removal
- Efficient and patient-friendly services for international patients
- Transparent pricing and internationally accredited hospitals
These advantages make Korea ideal for safe, precise, and effective kidney stone evaluation with CT urography.
Cost Range
Estimated costs for CT urography for kidney stones in Korea:
- Consultation: $20–$50
- Non-Contrast CT: $250–$500
- Contrast-Enhanced CT: $400–$700
- 3D Reconstruction Imaging: $100–$200
- Integration with Labs & Ultrasound: $350–$900
Costs vary depending on hospital, type of CT scan, and additional diagnostics or treatments required.
Popular Clinics in Korea
Top hospitals providing CT urography for kidney stones include:
- Seoul National University Hospital
- Asan Medical Center
- Samsung Medical Center
- Severance Hospital (Yonsei University)
- CHA Bundang Medical Center
- Wooridul Urology Clinic
These hospitals are recognized for precise imaging, expert diagnosis, and comprehensive care for both local and international patients.