Treatment Overview
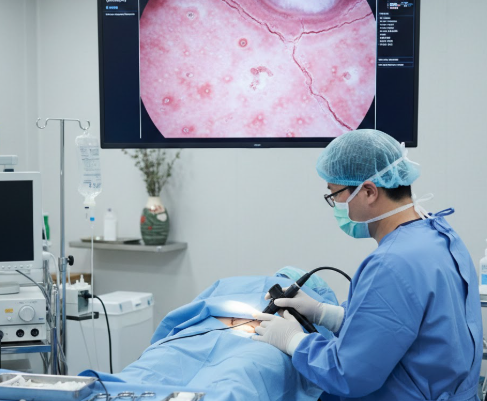
Cystoscopy is a critical diagnostic procedure used to evaluate interstitial cystitis (IC), a chronic bladder condition causing pelvic pain, urinary urgency, and frequency. By inserting a flexible or rigid endoscope through the urethra, urologists can directly visualize the bladder lining, identify inflammation, ulcers, or Hunner’s lesions, and take biopsies if necessary. In Korea, cystoscopy for IC is performed using advanced high-definition scopes and modern imaging techniques, providing accurate diagnosis and guiding effective treatment plans for both domestic and international patients.
Purpose & Benefits
The main purpose of cystoscopy in interstitial cystitis diagnosis is to confirm the condition and rule out other bladder disorders. Key benefits include:
- Direct visualization of bladder lining abnormalities such as Hunner’s lesions.
- Accurate diagnosis of interstitial cystitis versus other urinary tract conditions.
- Ability to perform bladder biopsies for further evaluation.
- Minimally invasive procedure with limited discomfort.
- Quick recovery with minimal downtime.
- Helps guide personalized treatment plans for IC management.
Ideal Candidates
Cystoscopy for interstitial cystitis is recommended for patients who:
- Experience chronic pelvic pain, urinary urgency, and frequency.
- Have bladder symptoms persisting for at least 6 weeks without clear infection.
- Exhibit negative urine culture results but continue to have urinary discomfort.
- Require confirmation of IC diagnosis to initiate advanced therapy.
- Are being evaluated for specialized treatments, such as bladder instillation therapy or laser therapy.
A consultation with a Korean urologist ensures that cystoscopy is appropriate and tailored to each patient’s condition.
Possible Risks & Complications
While cystoscopy for IC diagnosis is generally safe, potential risks include:
- Mild discomfort or burning sensation during urination after the procedure.
- Temporary blood in urine or minor bleeding at biopsy sites.
- Rare urinary tract infection, treatable with antibiotics.
- Rare urethral injury or bladder perforation.
Korean hospitals follow strict hygiene and safety protocols to minimize complications and ensure patient well-being.
Techniques & Technology Used
Korea employs advanced techniques for cystoscopy in interstitial cystitis diagnosis:
- Flexible Cystoscopy: Provides patient comfort during outpatient evaluation.
- Rigid Cystoscopy: Offers high-definition imaging for detailed examination and biopsy.
- High-Resolution Camera Systems: Real-time visualization of bladder lining abnormalities.
- Narrow Band Imaging (NBI): Enhances detection of subtle lesions and abnormal tissue.
- Hydrodistention during Cystoscopy: Helps reveal bladder changes associated with IC.
These technologies allow Korean urologists to accurately diagnose IC and plan targeted treatment.
Treatment Process in Korea
The cystoscopy procedure for interstitial cystitis diagnosis in Korea generally includes:
- Pre-procedure Evaluation: Urine tests, blood tests, and imaging to rule out infections or other conditions.
- Preparation: Local anesthesia is commonly applied; general anesthesia may be used in select cases.
- Cystoscopy Procedure: The scope is inserted through the urethra to examine the bladder. Biopsies or hydrodistention may be performed if necessary.
- Post-procedure Monitoring: Patients are observed briefly and usually discharged on the same day.
International patients receive dedicated support, including translators and hospital coordinators, ensuring a smooth experience.
Recovery & After-Care
Recovery after cystoscopy for interstitial cystitis diagnosis is generally quick, though some patients may experience mild temporary discomfort. Recommended after-care includes:
- Drinking plenty of water to flush the urinary tract.
- Avoiding strenuous physical activity for a few days.
- Monitoring for symptoms such as persistent bleeding, fever, or severe pain.
- Following prescribed medications, including antibiotics if necessary.
Follow-up appointments are scheduled to discuss cystoscopy findings and develop a personalized treatment plan.
Results & Longevity
Cystoscopy provides immediate and reliable visualization of the bladder, enabling accurate diagnosis of interstitial cystitis. When lesions or inflammation are detected, targeted treatment can begin promptly, improving long-term bladder health and quality of life. Patients with chronic IC may require periodic cystoscopy to monitor changes in bladder lining over time.
Why Korea Is a Top Destination
Korea is a leading destination for cystoscopy and interstitial cystitis diagnosis due to:
- Advanced Technology: High-definition flexible and rigid cystoscopes with imaging enhancements.
- Experienced Specialists: Board-certified urologists with expertise in chronic bladder conditions.
- Efficient Healthcare System: Short waiting times and streamlined diagnostic procedures.
- Medical Tourism Services: Comprehensive packages including hospital transfers, interpreters, and accommodations.
- Cost-Effective Care: Competitive pricing without compromising quality.
These factors make Korea an attractive choice for international patients seeking accurate and comprehensive IC evaluation.
Cost Range
The cost of cystoscopy for interstitial cystitis diagnosis in Korea varies depending on hospital and procedure complexity:
- Diagnostic Cystoscopy: $400 – $800 USD
- Cystoscopy with Biopsy or Hydrodistention: $800 – $1,500 USD
International patient packages often include hospital fees, translation services, and accommodation.
Popular Clinics in Korea
Top hospitals and clinics offering cystoscopy for interstitial cystitis diagnosis in Korea include:
- Severance Hospital, Seoul: Advanced urology department with international patient support.
- Asan Medical Center, Seoul: Cutting-edge diagnostic facilities for bladder disorders.
- Samsung Medical Center, Seoul: Specializes in minimally invasive bladder procedures.
- Bundang CHA Hospital, Seongnam: Outpatient cystoscopy with patient-centered care.
- Hanyang University Hospital, Seoul: Comprehensive urology services for both local and international patients.
These hospitals provide high-quality medical care with exceptional support for international patients.