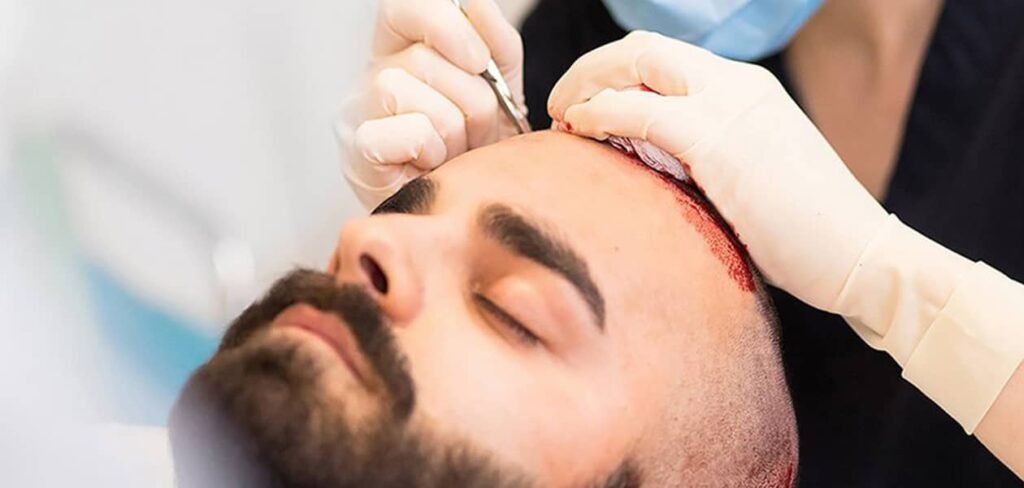
Hair transplant surgery—whether through FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) or FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation)—is a common cosmetic procedure with high success rates. However, for patients with underlying health conditions, it’s not without risks. If you have chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, autoimmune disorders, or are immunocompromised, you may face elevated risks that must be carefully assessed before undergoing surgery.
This comprehensive guide explains the medical risks of hair transplantation, how they affect patients with health conditions, and what can be done to minimize complications and promote safe healing.
🔍 Why Medical History Matters in Hair Transplant Surgery
Hair transplant procedures are typically performed under local anesthesia, but they still involve surgical trauma, vascular manipulation, and post-operative healing—all of which are affected by systemic health conditions. Patients with comorbidities must be properly evaluated to avoid complications such as:
- Delayed healing
- Infections
- Cardiovascular events
- Poor graft survival
A multidisciplinary approach involving your transplant surgeon, primary physician, and specialists is critical to safe outcomes.
⚠️ Common Medical Risks and How They Manifest
Below is a breakdown of risks by condition and what patients and clinicians should watch for:
1. Infection Risk (Especially in Diabetic or Immunosuppressed Patients)
Cause: Weakened immune defenses, poor wound healing.
Manifestations:
- Redness, swelling, or discharge at donor/recipient sites
- Fever or systemic symptoms
- Folliculitis (inflamed hair follicles)
Who’s at Risk:
- Diabetics
- Autoimmune patients on immunosuppressants
- Those with HIV/AIDS
Preventive Tips:
- Prophylactic antibiotics may be prescribed.
- Monitor glucose levels tightly pre- and post-op.
- Maintain strict scalp hygiene.
2. Poor Wound Healing or Necrosis
Cause: Inadequate blood supply, poor glucose control, or vascular disease.
Manifestations:
- Slow closure of donor area (especially in FUT)
- Dark, dry patches on scalp indicating ischemia
- Wound reopening or crusting that doesn’t resolve
Who’s at Risk:
- Patients with peripheral artery disease (PAD)
- Smokers
- Diabetics with poor circulation
Preventive Tips:
- Use of low-tension closure techniques for FUT
- PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) therapy to boost angiogenesis
- Avoid smoking and manage cholesterol/blood pressure
3. Cardiovascular Events
Cause: Anxiety, local anesthesia (especially with epinephrine), medication interactions.
Manifestations:
- Hypertension or hypotension during surgery
- Irregular heartbeat
- Chest discomfort or shortness of breath
Who’s at Risk:
- Patients with known cardiac history (arrhythmias, coronary artery disease)
- Patients on beta-blockers or anticoagulants
Preventive Tips:
- Pre-op clearance from a cardiologist
- Avoid epinephrine-based anesthesia if contraindicated
- Monitor vitals continuously during procedure
4. Medication Interactions
Cause: Conflict between prescribed drugs and surgical medications (antibiotics, anesthetics, anti-inflammatories).
Examples:
- NSAIDs may increase bleeding risk in patients on anticoagulants.
- Steroids can delay healing and increase infection risk.
- Immunosuppressants may reduce graft survival or increase scarring.
What to Do:
- Provide a complete medication list to your surgeon.
- Work with a pharmacist or physician to adjust regimens temporarily if needed.
5. Bleeding and Hematoma Formation
Cause: Blood thinners, high blood pressure, surgical trauma.
Manifestations:
- Swelling and bruising
- Visible blood accumulation under the scalp
- Persistent oozing at the donor or recipient site
Who’s at Risk:
- Patients on aspirin, warfarin, or direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs)
- Hypertensive patients
Preventive Tips:
- Pause anticoagulants before surgery (only with physician approval)
- Keep head elevated post-op
- Avoid heavy lifting and physical strain
6. Scarring and Keloid Formation
Cause: Genetic predisposition, excessive tension, poor healing.
Manifestations:
- Thick, raised scars (especially in FUT procedures)
- Itching, tenderness, or unsightly cosmetic outcome
Who’s at Risk:
- Patients with darker skin tones (higher keloid risk)
- Those with a personal or family history of keloids
Preventive Tips:
- Choose FUE over FUT if at risk for hypertrophic scarring
- Use silicone scar gels or steroid injections post-op
7. Flare-ups of Underlying Autoimmune Diseases
Cause: Surgical stress or immune stimulation.
Manifestations:
- Lupus flare (rash, joint pain, fatigue)
- Psoriasis or eczema outbreak at surgical site
- Alopecia areata recurrence
Who’s at Risk:
- Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Patients with alopecia areata or lichen planopilaris
Preventive Tips:
- Coordinate care with a rheumatologist or dermatologist
- Time surgery during disease remission
- Avoid transplanting into inflamed scalp areas
🩺 Pre-Operative Checklist for Medically Complex Patients
Before surgery, ensure the following are addressed:
| Requirement | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Full medical history | Include all chronic illnesses and past surgeries |
| Medication list | Include OTC, supplements, and prescription drugs |
| Blood tests | CBC, fasting glucose, coagulation profile, etc. |
| Specialist clearance | Cardiologist, endocrinologist, etc. as needed |
| Smoking and alcohol cessation | At least 2 weeks before and after surgery |
| Informed consent | Understand all risks, including condition-specific ones |
Final Thoughts
While hair transplant surgery can offer transformative results, it’s not without risks—especially for individuals with pre-existing health issues. The key to a safe and successful outcome is open communication with your surgical team, a thorough health screening, and careful postoperative care.
If you have health concerns, always consult both your primary doctor and a board-certified hair restoration surgeon before making a decision.