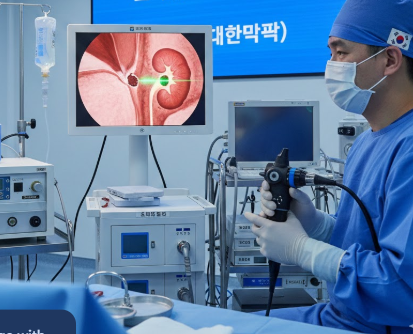
Ho:YAG Laser Stone Removal in Korea
Treatment Overview Holmium:YAG (Ho:YAG) Laser Stone Removal is one of the most advanced and effective treatments for urinary stones, including kidney stones, ureter stones, and
Get accurate and early detection of kidney stones with Korea’s advanced urology diagnostic services. Using high-resolution imaging such as CT scans, ultrasounds, and digital X-rays, Korean specialists precisely identify stone size, type, and location for effective treatment planning. Korea Beauty Guide connects international patients with trusted clinics offering fast, reliable, and noninvasive kidney stone diagnosis for optimal urinary tract health.

Treatment Overview Holmium:YAG (Ho:YAG) Laser Stone Removal is one of the most advanced and effective treatments for urinary stones, including kidney stones, ureter stones, and

Treatment Overview Kidney stones are a common urological condition that can lead to severe pain, urinary obstruction, and recurrent episodes if left untreated. Korea offers

Treatment Overview Kidney stones are a common urological condition that can cause severe pain, hematuria, and urinary obstruction. Accurate diagnosis is essential to determine stone

Treatment Overview Kidney stones often cause severe flank or abdominal pain, making effective pain management an essential part of care. Pain can be sudden and

Treatment Overview Kidney stones can sometimes cause sudden, severe pain and complications that require emergency evaluation. Symptoms such as intense flank pain, vomiting, hematuria, or
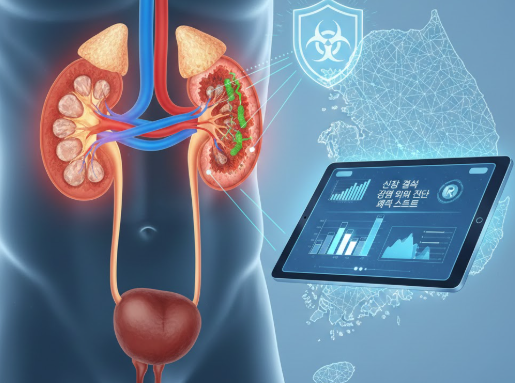
Treatment Overview Kidney stones can increase the risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs) by obstructing urine flow and providing a surface for bacterial growth. In

Treatment Overview Kidney stones can cause hematuria, or blood in urine, which is often the first noticeable symptom for patients. Hematuria can be visible (gross

Treatment Overview Kidney stones can pose a serious threat to kidney health, especially when recurrent or untreated, potentially leading to chronic kidney disease (CKD). CKD
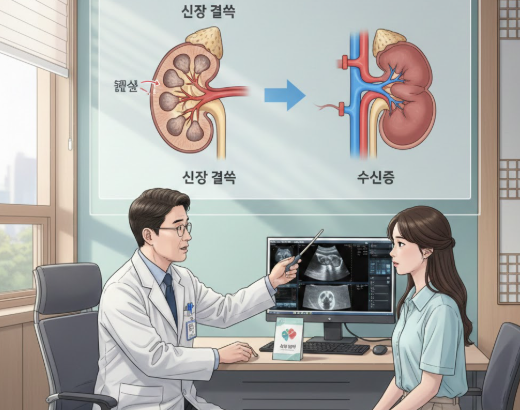
Treatment Overview Kidney stones can obstruct the urinary tract, causing urine to back up into the kidneys, a condition known as hydronephrosis. This can lead
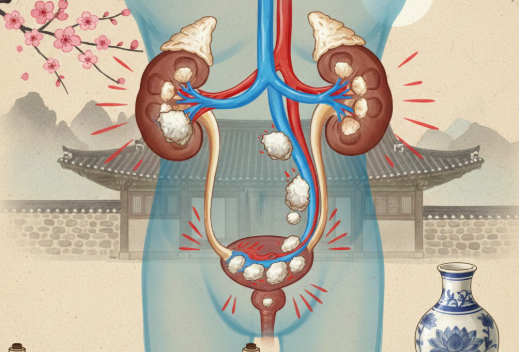
Treatment Overview Kidney stones are hard mineral deposits that can form in the kidneys and travel through the urinary tract. In some cases, stones cause

Treatment Overview Holmium:YAG (Ho:YAG) Laser Stone Removal is one of the most advanced and effective treatments for urinary stones, including kidney stones, ureter stones, and

Treatment Overview Kidney stones are a common urological condition that can lead to severe pain, urinary obstruction, and recurrent episodes if left untreated. Korea offers

Treatment Overview Kidney stones are a common urological condition that can cause severe pain, hematuria, and urinary obstruction. Accurate diagnosis is essential to determine stone

Treatment Overview Kidney stones often cause severe flank or abdominal pain, making effective pain management an essential part of care. Pain can be sudden and

Treatment Overview Kidney stones can sometimes cause sudden, severe pain and complications that require emergency evaluation. Symptoms such as intense flank pain, vomiting, hematuria, or

Treatment Overview Kidney stones can increase the risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs) by obstructing urine flow and providing a surface for bacterial growth. In

Treatment Overview Kidney stones can cause hematuria, or blood in urine, which is often the first noticeable symptom for patients. Hematuria can be visible (gross

Treatment Overview Kidney stones can pose a serious threat to kidney health, especially when recurrent or untreated, potentially leading to chronic kidney disease (CKD). CKD

Treatment Overview Kidney stones can obstruct the urinary tract, causing urine to back up into the kidneys, a condition known as hydronephrosis. This can lead

Treatment Overview Kidney stones are hard mineral deposits that can form in the kidneys and travel through the urinary tract. In some cases, stones cause