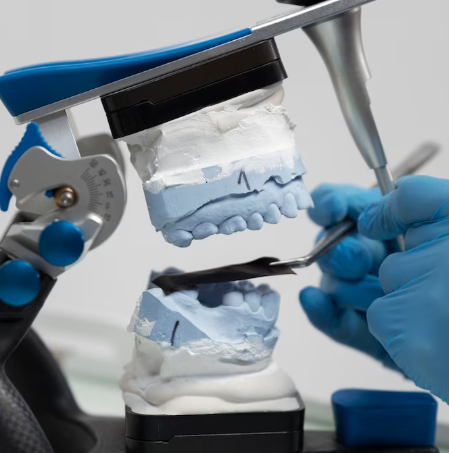
Treatment Overview
Orthognathic Surgery with 3D Simulation in Korea refers to jaw corrective procedures (upper jaw, lower jaw, or both) that are planned and executed using advanced three-dimensional imaging, virtual surgical simulation (VSS), CAD/CAM surgical guides, 3D printing and digital transfer workflows. In Korea, leading surgeons combine orthodontic alignment, bite correction, aesthetic facial balancing and digital surgical precision to achieve predictable, efficient, and high-quality outcomes.
Traditional orthognathic surgery relied on 2-D cephalometry, model surgery and manual splints; today the Korean model emphasises full 3-D workflows: CBCT/CT scans, intra-oral scans, virtual simulation, custom surgical splints/plates, and post-operative verification. sciencedirect.com+3synapse.koreamed.org+3mdpi.com+3
This digital approach improves accuracy, reduces human error, enhances patient communication (showing the simulation before surgery) and allows for better aesthetic and functional outcomes.
Purpose & Benefits
Purpose
- Correct skeletal jaw misalignments (overbite, underbite, open bite, crossbite) through orthognathic surgery.
- Use 3-D simulation to visualise both functional and aesthetic outcomes (jaw repositioning, bite relationship, facial profile).
- Coordinate orthodontic treatment (braces, clear aligners) with surgical correction for full skeletal-dental harmony.
- Pre-plan the surgery virtually to optimise bone movements, minimise risk, and fabricate precise surgical guides/splints.
- Improve patient understanding and consent by showing the planned outcome in 3D.
Benefits
- Higher Accuracy: Studies show linear discrepancies of around ~1 mm and angular <2° when 3-D simulation & digital workflow are used. mdpi.com+1
- Predictability: Virtual simulations allow the surgeon and patient to preview results and refine the plan.
- Better Efficiency: Digital fabrication of splints, guides and surgical plates streamlines the intra-operative steps.
- Enhanced Aesthetics & Function: Jaw repositioning is aligned with facial profile planning and dental occlusion concurrently.
- Improved Patient Communication: Seeing a 3-D model and simulation helps patients understand the treatment plan better.
- Lower Error Rates: Use of CAD/CAM and digital transfer reduces manual model errors from traditional methods. koreascience.kr
Ideal Candidates
- Patients with skeletal malocclusion (Class II, Class III), asymmetry of jaws, or significant bite discrepancy.
- Those requiring both functional correction (bite, chewing, speech) and aesthetic improvement (jawline, profile).
- Orthodontic patients whose treatment plan includes surgical jaw correction and require precise digital coordination.
- Adult patients seeking high-precision jaw surgery in Korea with minimal guess-work and maximum predictability.
- International patients willing to travel for premium digital orthognathic care, combining orthodontics + surgery.
Possible Risks & Complications
Even with advanced 3-D simulation workflows, orthognathic surgery carries risks — but Korean centres mitigate these with digital precision. Potential issues include:
- Post-operative swelling, bruising, numbness of lip/cheek/chin.
- Temporary changes in bite or speech during healing.
- Surgical relapse (rare) if bone healing or fixation fails.
- Simulation mis-prediction (rare) — though error margins in digital planning are very small (~1 mm).
- Cost and treatment time may be higher due to advanced digital planning and fabrication.
Korea’s utilisation of cloud-based collaboration, digital verification, CAD/CAM guides and post-operative 3D assessment further decreases risk and increases outcome reliability. mdpi.com+1
Surgical Techniques Used
- 3D CBCT / CT & Intraoral Scan Acquisition: Combined data of bone, teeth, soft tissue.
- Virtual Surgical Planning (VSP) / Computer-Aided Surgical Simulation (CASS): Surgeons simulate osteotomies, reposition bone segments, predict soft-tissue changes. synapse.koreamed.org+1
- CAD/CAM Splint & Guide Fabrication: 3D-printed surgical wafers, cutting guides, repositioning guides for exact intraoperative implementation. koreascience.or.kr
- Navigation / Digital Transfer: The virtual plan is transferred to the surgery via guides or navigation tools.
- Orthodontic Integration: Pre-surgical orthodontic alignment + post-surgical fine-tuning with braces or aligners.
- Post-operative 3D Verification: After surgery, scanning and overlay compare actual outcome vs planned simulation. Example: translational discrepancy ~0.61-1.00 mm; angular ~0.50-1.43° in one Korean study. mdpi.com
Recovery & Aftercare
- Soft/modified diet for first 1-2 weeks; gradual return to normal food.
- Oral hygiene and wound care as per surgeon’s instruction.
- Swelling and bruising typically peak at day 2-3, then reduce.
- Orthodontic treatment resumes/integrates post-surgery as planned.
- Digital follow-up: some centres perform CBCT or intraoral scans at specified intervals to ensure alignment and healing.
- Return to regular activities typically in 2-4 weeks; full skeletal stability may take 3-6 months depending on case.
- Long-term maintenance: orthodontic retainers, dental check-ups, jaw joint monitoring if needed.
Results & Longevity
Expected Results
- Precise jaw repositioning aligning facial profile, symmetry, and bite.
- Improved chewing function, speech, airway/respiratory function (in some cases).
- Balanced facial aesthetics and better profile/contour.
- Reduced treatment surprises thanks to pre-surgical simulation.
Longevity
- When fixation is stable and healing is good, surgical corrections are permanent.
- Digital planning enhances long-term stability by reducing error.
- Orthodontic follow-up ensures occlusal alignment remains intact.
- Many Korean centres report high success and patient satisfaction for digital orthognathic workflows.
Why Korea Is a Top Destination
- Korean surgical centres lead in computer-assisted orthognathic surgery (CAOS) and digital jaw correction techniques. sciencedirect.com
- Pioneering research from Korean universities shows evolution of full-digital workflows and high accuracy. mdpi.com
- Advanced infrastructure: CBCT, intraoral scanning, 3D printing labs, CAD/CAM fabrication in many hospitals.
- High international standards combined with competitive pricing for global patients.
- Multilingual staff, international patient services, combined orthodontic-surgical teams.
- Strong aesthetic and functional focus — not just bite correction, but facial harmony and cosmetic outcomes.
Unique Korean Methods & Technology
- Cloud-based platforms for surgeon/engineer collaboration on surgical plans. mdpi.com
- Reproduction of natural head position (NHP) and simulation in 3-D for accurate transfer. mdpi.com+1
- Use of CAD/CAM custom surgical splints, cutting/repositioning guides.
- Navigation-assisted orthognathic surgery in selected centres.
- Digital verification of outcomes with overlay of pre- and post-operative 3-D models.
- Integration of orthodontic alignment, surgical correction, and aesthetic design in one workflow.
Cost Considerations
Cost varies widely depending on case complexity, surgical scope (single vs double jaw), orthodontic integration, and digital workflow level.
- Basic surgical correction with digital planning: moderate range.
- Double-jaw (bimaxillary) with full 3D simulation, navigation, CAD/CAM guides: higher end.
- Additional costs: orthodontic phase, travel/accommodation (for international patients), post-op care.
It’s important to request full breakdown: imaging, virtual simulation, surgical guides, hospital/OR fees, orthodontic treatment, follow-ups.