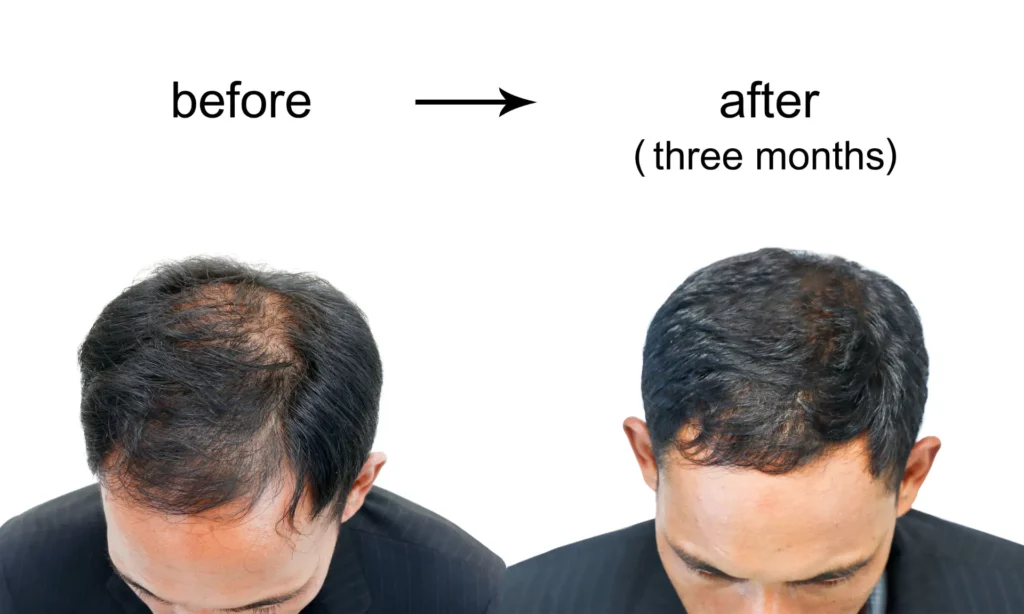
Hair loss is a common concern for millions of men worldwide. While some degree of shedding is natural, excessive or sudden hair loss can be distressing. Understanding the underlying causes is the first step toward effective treatment. In this post, we’ll explore the top 10 causes of hair loss in men, providing the knowledge you need to take action.
1. Genetics (Androgenetic Alopecia)
The most common cause of hair loss in men is male pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia. This hereditary condition usually starts with a receding hairline and thinning at the crown, progressing over time.
- Key Sign: Gradual hair thinning, usually starting at the temples or crown.
- Solution: FDA-approved treatments like minoxidil (Rogaine) and finasteride (Propecia) can help slow progression. Hair transplants may be considered for more advanced cases.
2. Hormonal Imbalance
Hormonal changes, particularly elevated levels of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), can shrink hair follicles and shorten the hair growth cycle.
- Key Sign: Diffuse thinning or patterned loss.
- Solution: Hormone-modulating treatments like finasteride or DHT blockers may be recommended under a doctor’s supervision.
3. Nutritional Deficiencies
A lack of essential nutrients can weaken hair structure and disrupt growth.
- Common Deficiencies: Iron, zinc, vitamin D, biotin, and protein.
- Key Sign: General thinning, brittle or dull hair.
- Solution: Blood tests can identify deficiencies. A balanced diet or targeted supplementation can restore hair health.
4. Stress (Telogen Effluvium)
Physical or emotional stress can push hair follicles into the resting (telogen) phase, causing noticeable shedding.
- Key Sign: Sudden shedding 2–3 months after a stressful event.
- Solution: Hair usually regrows within 6–9 months once the stressor is resolved. Stress management and healthy habits can help prevent recurrence.
5. Medical Conditions
Certain diseases can trigger hair loss either directly or as a side effect of treatment.
- Examples: Thyroid disorders, lupus, diabetes, and anemia.
- Key Sign: Diffuse hair thinning or patchy loss, often accompanied by other symptoms.
- Solution: Treating the underlying condition often improves hair growth.
6. Medications
Hair loss can be a side effect of certain medications.
- Common Culprits: Chemotherapy drugs, beta-blockers, antidepressants, blood thinners, and anabolic steroids.
- Key Sign: Sudden or diffuse thinning after starting new medication.
- Solution: Consult your doctor about alternatives or adjustments.
7. Infections and Scalp Conditions
Scalp infections and dermatologic issues can hinder hair growth.
- Examples: Ringworm (fungal infection), seborrheic dermatitis, psoriasis.
- Key Sign: Itching, redness, scaling, or inflamed patches on the scalp.
- Solution: Antifungal or medicated treatments prescribed by a dermatologist.
8. Autoimmune Disorders (Alopecia Areata)
In conditions like alopecia areata, the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles.
- Key Sign: Sudden, round patches of hair loss on the scalp or beard.
- Solution: Treatments include corticosteroids, immunotherapy, or topical agents to stimulate growth.
9. Poor Hair Care Practices
Excessive heat styling, chemical treatments, tight hairstyles, and harsh grooming habits can damage hair shafts and roots.
- Key Sign: Breakage, split ends, thinning edges.
- Solution: Adopt gentle hair care practices, reduce heat exposure, and avoid traction hairstyles like tight ponytails or braids.
10. Aging
As men age, hair growth naturally slows and follicles may shrink or stop producing new hairs.
- Key Sign: Gradual thinning and graying.
- Solution: While age-related hair loss is natural, treatments like PRP therapy, low-level laser therapy (LLLT), or hair transplants can help restore volume.
Final Thoughts
Hair loss in men can result from a combination of genetic, hormonal, environmental, and lifestyle factors. The good news is that many forms of hair loss are treatable or manageable with the right diagnosis and intervention.
If you’re experiencing hair loss, consult with a dermatologist or hair restoration specialist to uncover the root cause and explore your treatment options. Early action can make a big difference in preserving your hair and confidence.